Intro to Jupyter R on NeSI
Written and presented by Ludovic Dutoit
install a package in R on Jupyter
To run this example, you will need to log on to JupyterHub, and launch an R notebook:

try loading an uninstalled library from a Jupyter R 4.0.1 notebook
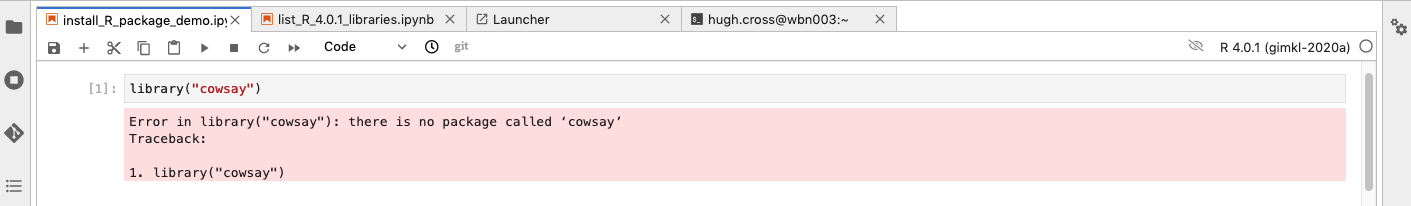
It is worth trying first because a lot of things are pre-installed:
Here is a list of all R libraries on R 4.0.1
If you try installing something from within the R notebook on Jupyter, it won’t work:
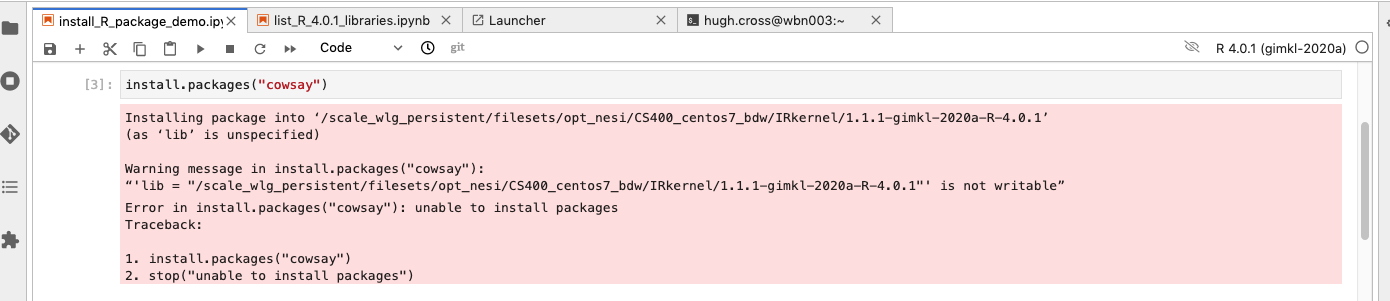
This is the trap! The solution is not too complicated but there is no other easy work around.

You actually need to:
- Go in the terminal (can be done from the jupyter notebook)
- Find and load the version of R used on jupyter notebook
- Install your package
module spider R # find the version
module load R R/4.0.1-gimkl-2020a #load the version
Open R by running R in the terminal and you should now be able to install and load the package (after choosing a CRAN session)
R
install.packages("cowsay")
library("cowsay")
If you now get back into the notebook or the console, you can access this package.
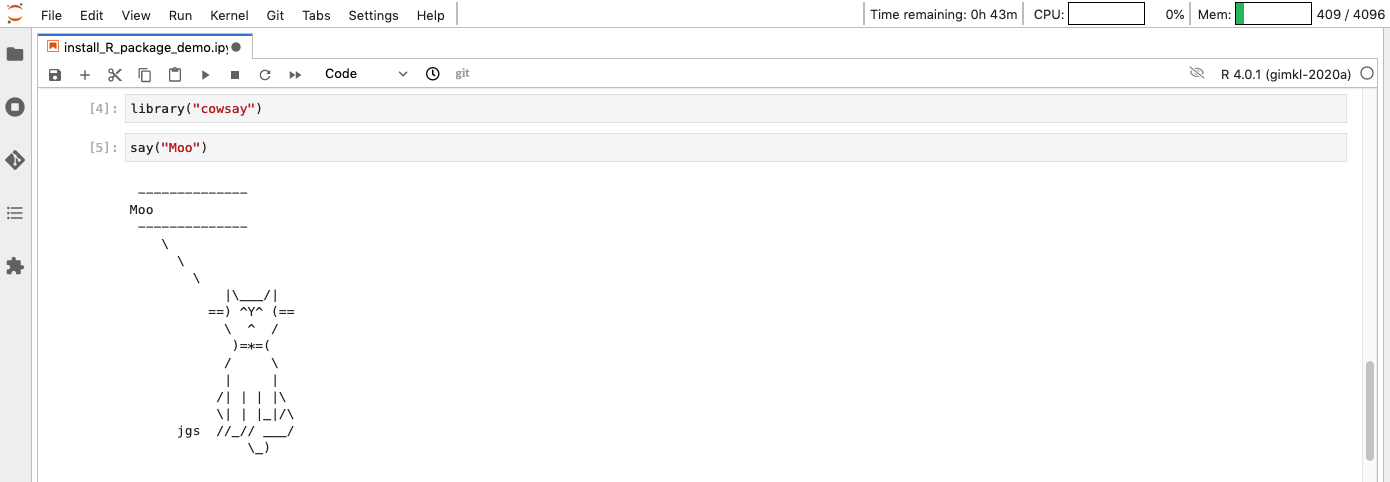
Very good, but I was led to believe it would be a cow:
Okay, we are getting distracted here.
Be aware that a package installed for one version of R would need to be re-installed for a different R version. If you remember having installed a package but R cannot find it, you are likely to be using the wrong R version.
R jobs
A job file cannot be an Rscript. You will prepare a bash job file that run an Rscript.
Using nano or the jupyter text editor we can create a basic R script making a simple plot. Let’s call it testscript.R and fill it with:
png(filename="plot.png") # This line redirects plots from screen to plot.png file.
# Define the cars vector with 5 values
cars <- c(1, 3, 6, 4, 9)
# Graph the cars vector with all defaults
plot(cars)
Now let’s make a bash file that can run it run_testscript.sh
#!/bin/bash -e
#SBATCH --account uoo00116 # CHANGE
#SBATCH --job-name runtestscriptR
#SBATCH --time 00:01:00
#SBATCH --mem 512MB
#SBATCH --qos debug
module load R/4.0.1-gimkl-2020a
# Help R to flush errors and show overall job progress by printing
# "executing" and "finished" statements.
echo "Executing R ..."
srun Rscript testscript.R
echo "R finished."
You can now submit that run_testscript.sh file that will run the testscript.R.
sbatch run_testscript.sh
squeue -u $USER #will show you th queue of jobs, if it is emopty, it ran or bugged
You should have a plot.png file in your directory.
In summary, I hope you’ll remember the cowsay R package and maybe other things!
Here is a web version of the Jupyter notebook used for this session